Table of Contents
Zombie Cells The concept of Zombie Cells in relation to aging and disease unveils a fascinating yet concerning aspect of cellular biology. These Zombie Cells, also known as senescent cells, linger in tissues and contribute to a cascade of detrimental effects that accelerate aging and pave the way for various age-related diseases. This exploration delves into the mechanisms, implications, and emerging strategies to combat the impact of Zombie Cells on human health.
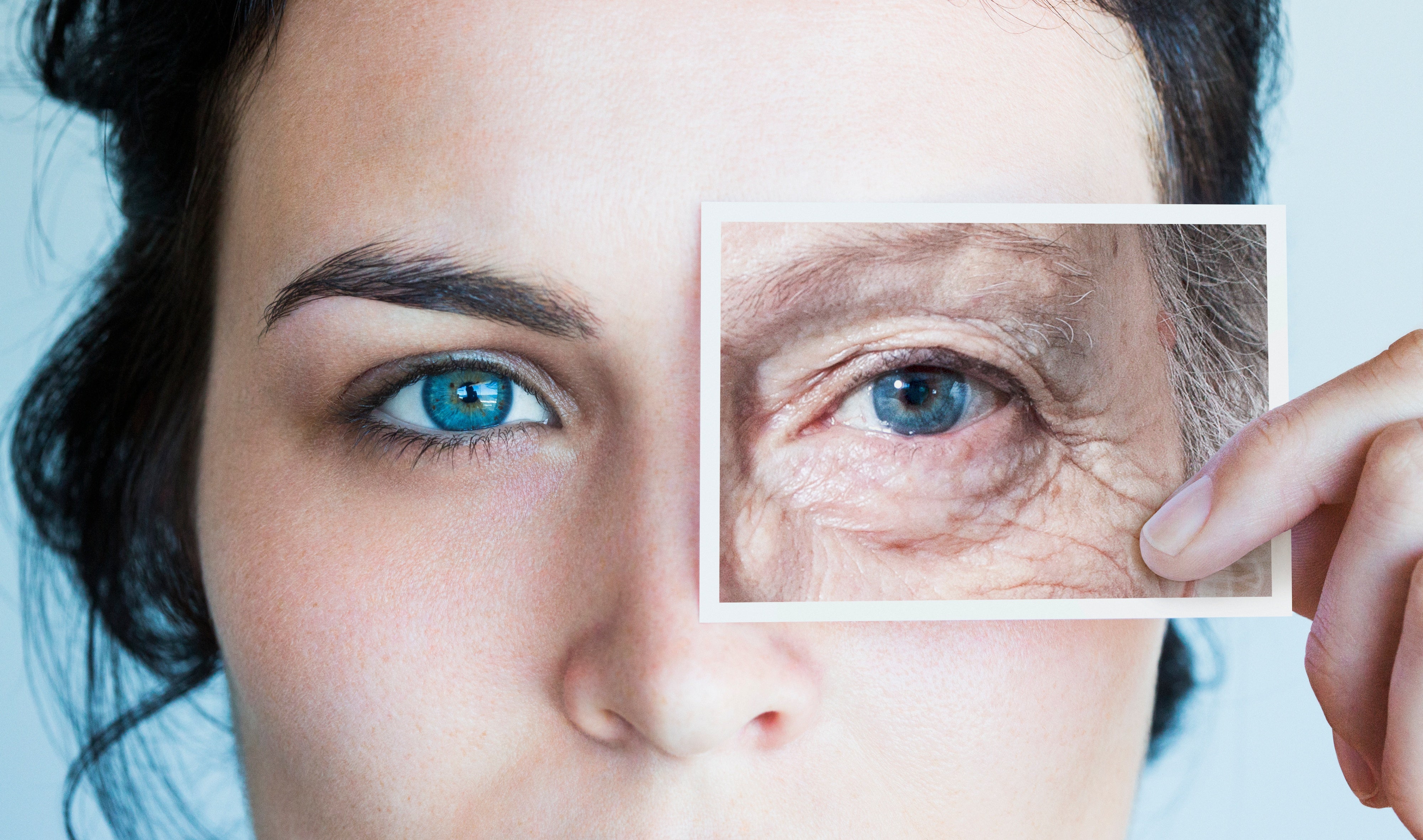
Unveiling Zombie Cells
Senescence: The Beginning of Zombie Cells
Zombie Cells originate from normal cells that undergo senescence, a state where they cease to divide but remain metabolically active. Initially, senescence serves as a protective mechanism against cancer by halting the replication of damaged cells.
Accumulation Over Time
However, Zombie Cells accumulate in tissues with age due to factors such as DNA damage, oxidative stress, inflammation, and genetic predisposition. Their persistence contributes to chronic inflammation and tissue dysfunction, hallmarks of aging.
Mechanisms Driving Aging and Disease
Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP)
One of the key features of Zombie Cells is their adoption of SASP, where they secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, growth factors, and matrix metalloproteinases. SASP disrupts tissue structure, promotes chronic inflammation, and contributes to age-related pathologies.
Immune System Dysfunction
The immune system’s ability to clear Zombie Cells declines with age, allowing these cells to accumulate further. This immune dysfunction exacerbates chronic inflammation and compromises tissue repair and regeneration processes.
Impact on Aging Tissues and Organs
Tissue Degeneration
In various organs such as the skin, joints, and cardiovascular system, Zombie Cells contribute to tissue degeneration. Their presence disrupts normal tissue architecture, reduces elasticity, and impairs organ function over time.
Musculoskeletal Decline
Zombie Cells play a role in musculoskeletal aging by promoting cartilage degradation in joints and contributing to the loss of muscle mass and strength. These changes increase the risk of conditions like osteoarthritis and sarcopenia.
Link to Age-Related Diseases
Cardiovascular Health
In the cardiovascular system, Zombie Cells promote atherosclerosis by contributing to inflammation within blood vessel walls. This inflammation accelerates plaque formation, narrowing arteries, and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Neurodegenerative Disorders
Zombie have implications for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Their presence in the brain contributes to neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction, exacerbating cognitive decline and impairing brain function.
Emerging Strategies to Combat Zombie Cells
Senolytics: Clearing the Undead
Senolytics are compounds that selectively target and eliminate Cells without harming healthy cells. These treatments show promise in rejuvenating aging tissues, improving organ function, and extending healthspan in preclinical studies and early clinical trials.
Senescent Cell-Targeted Therapies
Researchers are exploring various approaches to target senescent cells, including immunotherapies, gene therapies, and nanoparticle-based delivery systems. These therapies aim to enhance immune clearance of Zombie Cells and mitigate their detrimental effects.
Lifestyle Interventions
Diet and Nutrition
Certain dietary components, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods, may help reduce Zombie burden and support healthy aging. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can provide nutrients that mitigate cellular damage and promote longevity.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is beneficial for reducing Cell accumulation and promoting immune function. Physical activity improves circulation, enhances tissue repair mechanisms, and supports overall cellular health, contributing to healthier aging.
Future Directions in Research
Biomarkers of Senescence
Identifying biomarkers of Zombie could facilitate early detection and monitoring of senescent cell burden in individuals. Biomarker discovery may pave the way for personalized anti-aging strategies and targeted therapies to combat age-related diseases.
Longevity and Quality of Life
Advancements in understanding Cells and their role in aging offer opportunities to extend healthspan, the period of life spent in good health. By targeting cellular senescence, researchers aim to enhance both longevity and quality of life in aging populations.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical Implications of Anti-Aging Therapies
The pursuit of therapies targeting Zombie Cells raises ethical considerations regarding accessibility, affordability, and equitable distribution. Addressing these concerns ensures that anti-aging interventions benefit diverse populations and uphold ethical standards in healthcare.
Zombie Cells
Understanding the impact of Zombie Cells on aging and disease opens avenues for innovative therapies and interventions aimed at promoting healthy aging. By targeting senescent cells, researchers and healthcare providers can potentially mitigate age-related decline, enhance organ function, and improve overall well-being in aging populations. Embrace the knowledge of Zombie and their implications for aging gracefully, free from the burdens of chronic diseases associated with cellular senescence.





More Stories
How Inflammaging Impacts Your Health as You Age
The Art of Aging: Strategies for Thriving Through the Aging Process
How Geroscience Is Redefining the Golden Years